Trafficking mechanisms supporting interleukin-1β secretion revealed
New research from Inflammasome Lab reveals trafficking mechanisms driving the unconventional secretion of mature interleukin-1β in non-pyroptotic and pyroptotic myeloid cells, and functions for caspase-1 and Gasdermin-D therein.
Monteleone M, Stanley AC, Chen KW, Brown DL, Bezbradica JS, von Pein JB, Holley CL, Boucher D, Shakespear MR, Kapetanovic R, Rolfes V, Sweet MJ, Stow JL, Schroder K. (2018).
Interleukin-1β Maturation Triggers Its Relocation to the Plasma Membrane for Gasdermin-D-Dependent and -Independent Secretion. Cell Reports Aug 7;24(6):1425-1433. Pubmed.
Abstract
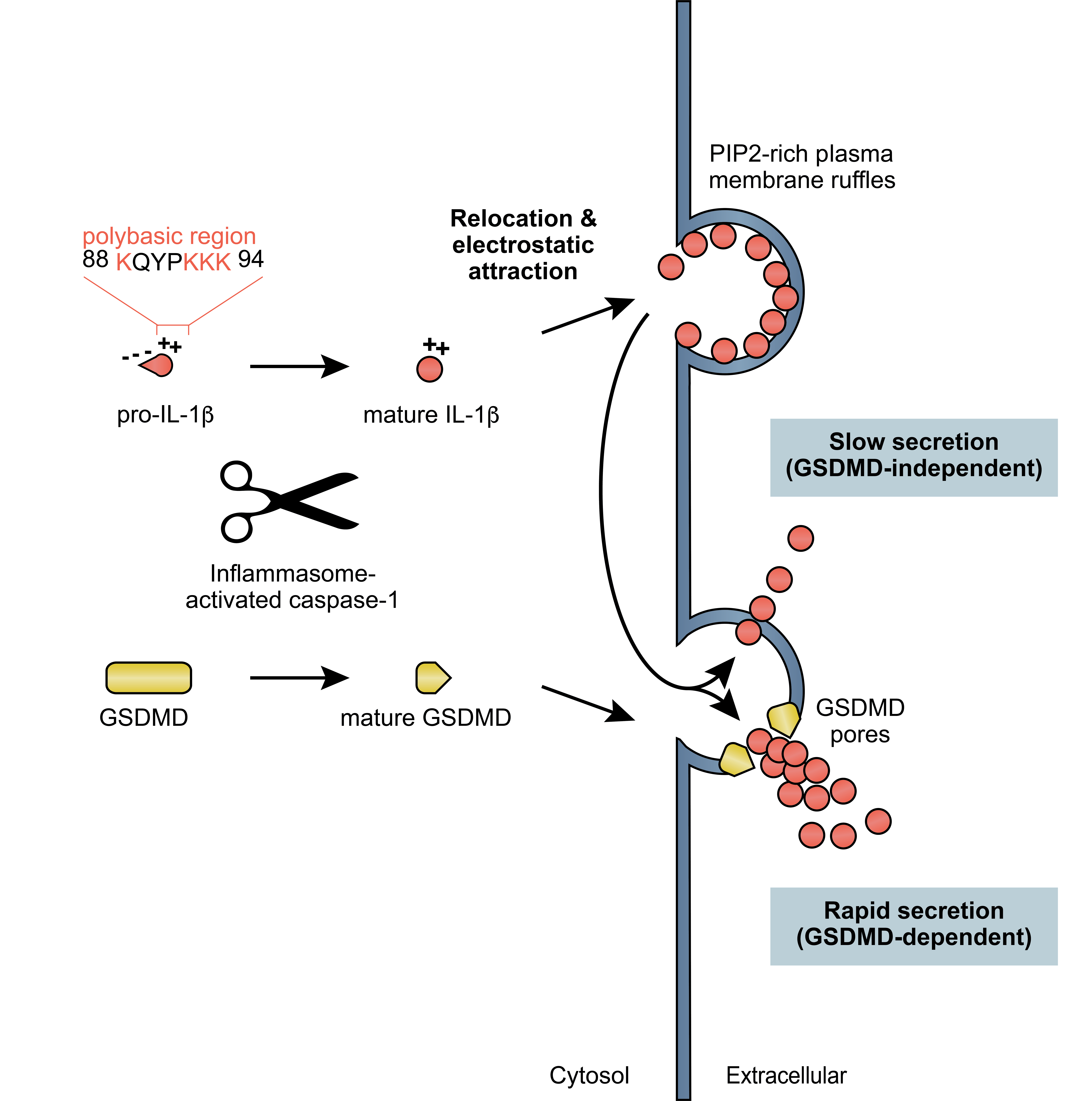
IL-1β requires processing by caspase-1 to generate the active, pro-inflammatory cytokine. Acute IL-1β secretion from inflammasome-activated macrophages requires caspase-1-dependent GSDMD cleavage, which also induces pyroptosis. Mechanisms of IL-1β secretion by pyroptotic and non-pyroptotic cells, and the precise functions of caspase-1 and GSDMD therein, are unresolved. Here, we show that, while efficient early secretion of endogenous IL-1β from primary non-pyroptotic myeloid cells in vitro requires GSDMD, later IL-1β release in vitro and in vivo proceeds independently of GSDMD. IL-1β maturation is sufficient for slow, caspase-1/GSDMD-independent secretion of ectopic IL-1β from resting, non-pyroptotic macrophages, but the speed of IL-1β release is boosted by inflammasome activation, via caspase-1 and GSDMD. IL-1β cleavage induces IL-1β enrichment at PIP2-enriched plasma membrane ruffles, and this is a prerequisite for IL-1β secretion and is mediated by a polybasic motif within the cytokine. We thus reveal a mechanism in which maturation-induced IL-1β trafficking facilitates its unconventional secretion.
Read more about this discovery in IMB News.
Copyright © 2017 - The University of Queensland